Micro Price Floor Deadweight Loss

Some of the major causes of deadweight losses include rent control price ceiling minimum wage price floor and taxation.
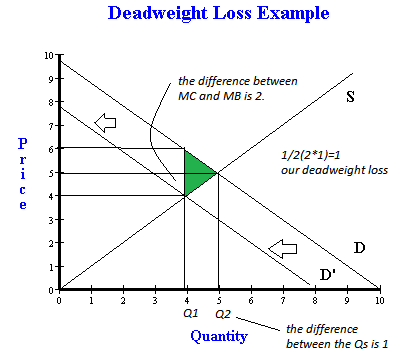
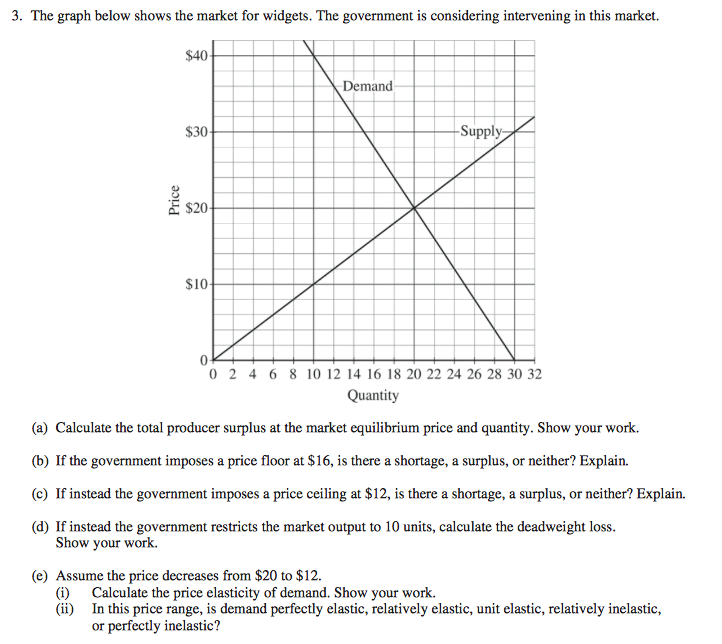
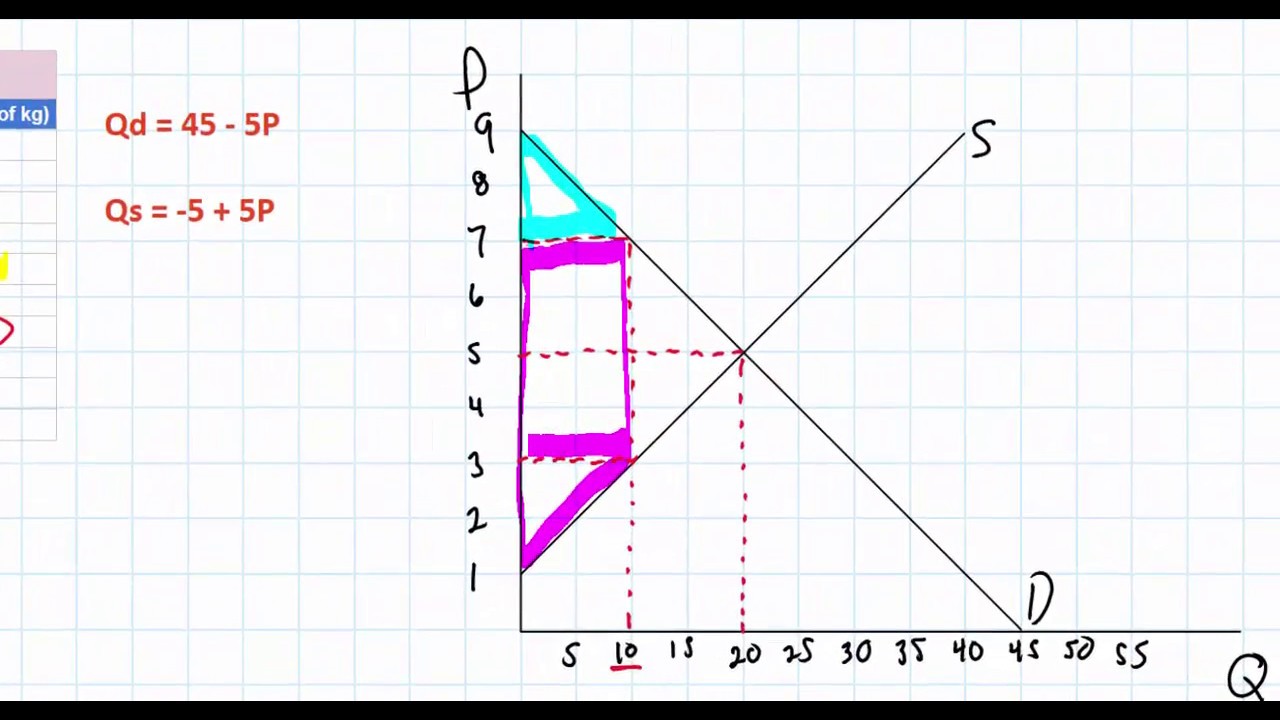
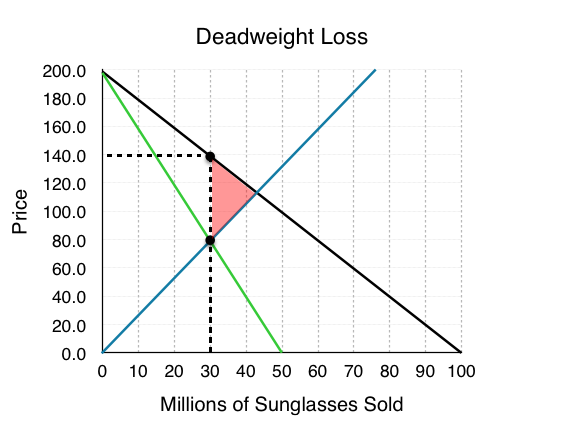
Micro price floor deadweight loss. This is the currently selected item. In the absence of externalities both the price floor and price ceiling cause deadweight loss since they change the market quantity from what would occur in equilibrium. A b h 2 large frac bh 2 2 b h sources of market failure deadweight loss. The deadweight welfare loss is the loss of consumer and producer surplus.
Taxes and perfectly elastic. An example of a price floor would be minimum wage. In other words deadweight loss indicates that the economic welfare of society is not at its optimum level. An example of a price ceiling would be rent control setting a maximum amount of money that a landlord can.
Causes of deadweight loss. How price controls reallocate surplus. Minimum wage and price floors. Once again deadweight loss are mostly triangles and can be calculated using the formula.
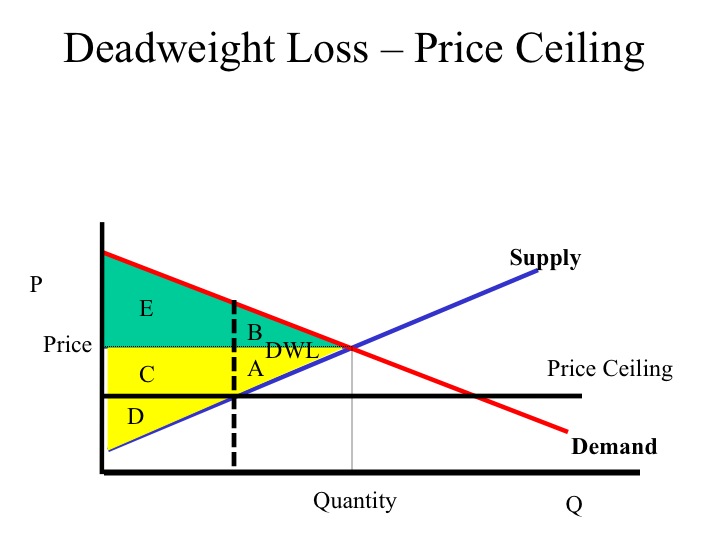
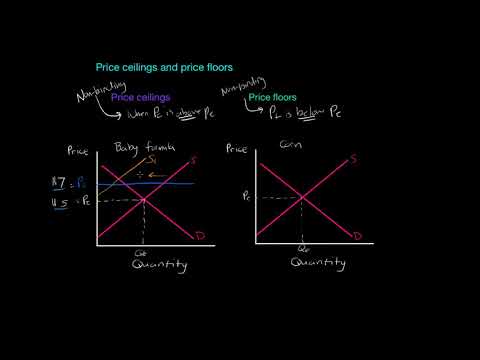
Example breaking down tax incidence. A deadweight welfare loss occurs whenever there is a difference between the price the marginal demander is willing to pay and the equilibrium price. Price ceilings and price floors. Creates a black market.
Non optimal production can be caused by monopoly pricing in the case of artificial scarcity a positive or negative externality a tax or subsidy or a binding price ceiling or price floor such as a minimum wage. Percentage tax on hamburgers. Price ceilings such as price controls and rent controls. Price and quantity controls.
Problems with rent ceiling. This is accompanied by a transfer of surplus from one player to another. Please try again later. A government law that makes it illegal to charger lower than the specified price.
The government sets a limit on how low a price can be charged for a good or service. Limiting the amount of quantity produced or putting a cap on prices can block adjustments to market equilibrium which leads to underproduction. Deadweight loss also known as excess burden is a measure of lost economic efficiency when the socially optimal quantity of a good or a service is not produced. Taxation and dead weight loss.
Mainly used in economics deadweight loss can be applied to any deficiency caused by an inefficient allocation of resources. Minimum wage and price floors deadweight loss this feature is not available right now. Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand. Price quantity control.
Price floors cause a deadweight welfare loss.