Measuring Hardness Of Ceramics

The method for measuring the hardness of fine ceramics is defined in jis r 1610 iso 14705.
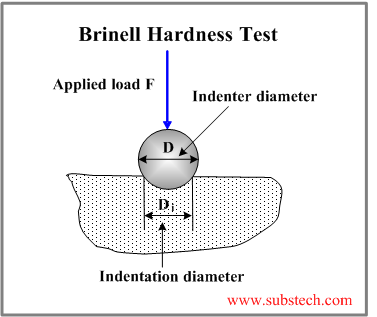
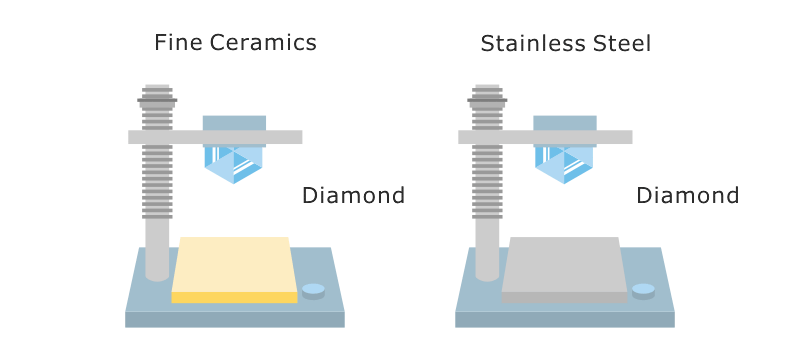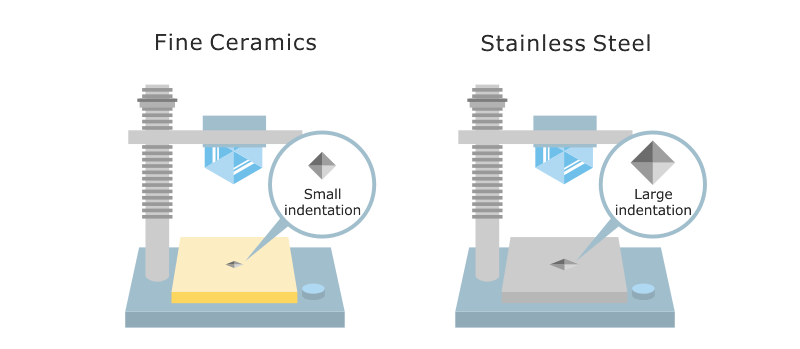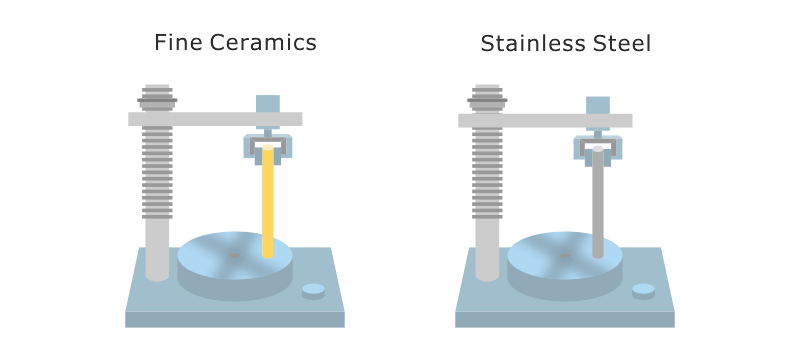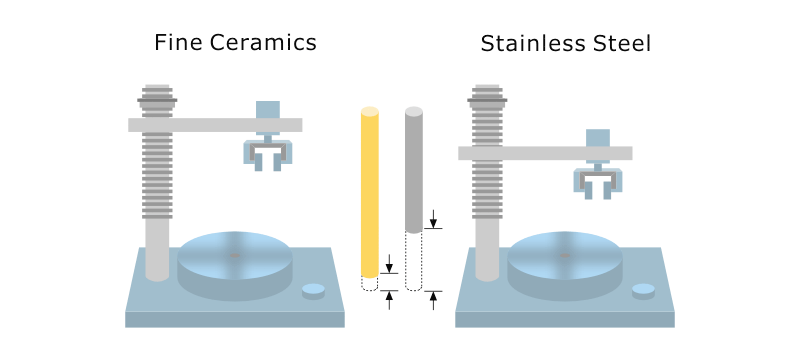
Measuring hardness of ceramics. Vickers hardness is a resistance value obtained by pressing a diamond indenter onto a test specimen. Vickers indentations are rarely made for hardness measurements in glasses and no astm or iso standards have been written for glass. The hardness of fine ceramics is generally indicated using a vickers hardness number. 1 the quotient of the load and the area of the residual indentation impression are regarded as the measure of hardness.
Hk 14 229 f d. Hardness of advanced ceramics and recommends a load of 9 8 n 1 kgf. This type of hardness is related to elasticity. The knoop number hk is calculated by the formula.
The standard deviation of the hardness of tiles from fig. For soft tile with up to a 1 kg load the hardness was 500 600 mpa with a standard deviation of 60 140 mpa. Rebound hardness also known as dynamic hardness measures the height of the bounce of a diamond tipped hammer dropped from a fixed height onto a material. The loading force in the knoop method are usually in the range of 10 gf to 1000gf micro hardness range.
Up to 2 kg for hard tiles the hardness was determined to 2 5 3 0 gpa. The knoop hardness test is applied for testing soft material and thin coating since the penetration depth is very small about 1 30 of the impression length. The optical resolution limits are estimated to be only 1 0l 2 na or 0 4 microns for vickers. The device used to take this measurement is known as a scleroscope.