Mats Alternative Splicing

Alternative splicing as is an important mechanism of eukaryotic gene regulation.
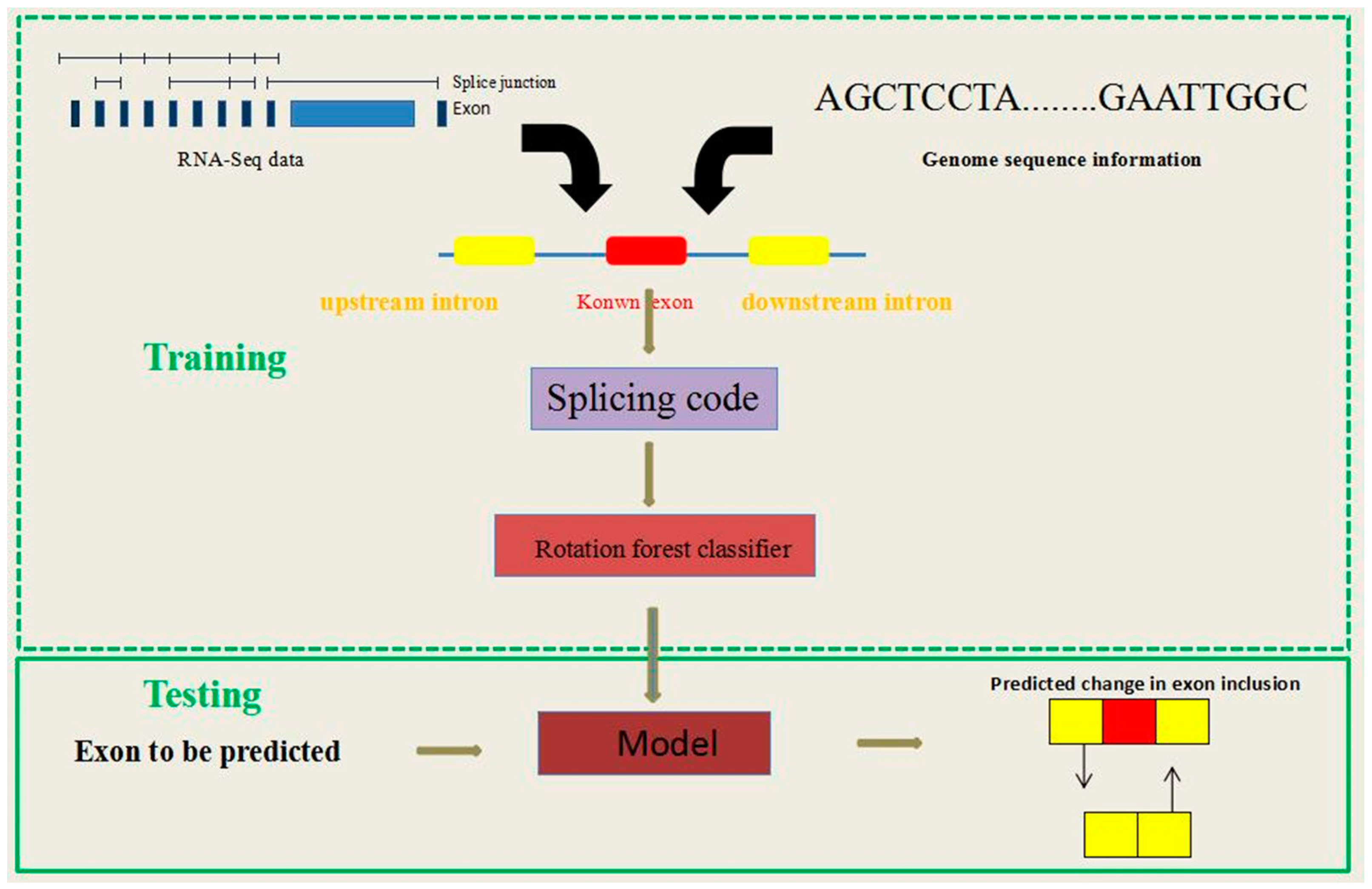
Mats alternative splicing. Mats is a computational tool to detect differential alternative splicing events from rna seq data. The statistical model of mats calculates the p value and false discovery rate that the difference in the isoform ratio of a gene between two conditions exceeds a given user defined threshold. I aligned adapter trimmed paired end reads using star and used sorted bam files as input to mats for the analysis of splicing events. In the analysis of alternative 5 or 3 splice sites the counts of junction reads that uniquely support the two competing splice sites can serve as the input for mats.
With the increasing capacity of high throughput sequencers it has become common for rna seq studies of as to examine multiple biological replicates. In exon skipping an exon is spliced out of the transcript together with its flanking introns. Given i provide average insert length r1 and r2 and the corresponding sd1 and sd2 values to mats does the read length should. Skipped exons se alternative 5 donor splice sites a5ss alternative 3 acceptor splice sites a3ss retained introns ri and mutually exclusive exon usage mxe.
Each alternative splicing event type has a corresponding set of output files. In the filename templates below as event is replaced by one of se skipped exon mxe mutually exclusive exons a3ss alternative 3 splice site a5ss alternative 5 splice site ri retained intron for the event specific filename. The statistical model of mats calculates the p value and false discovery rate that the difference in the isoform ratio of a gene between two conditions exceeds a given user defined threshold. The mats algorithm can be naturally extended to other types of alternative splicing events such as alternative 5 or 3 splice sites and mutually exclusive exon usage.
Significance alternative splicing as is an important mechanism of eukaryotic gene regulation. Here we report a new statistical model and computer program replicate mats rmats designed for analysis of replicate rna seq data. Deep rna sequencing rna seq has become a powerful approach for quantitative profiling of as. We previously developed multivariate analysis of transcript splicing mats a statistical method for detecting differential alternative splicing between two rna seq samples.
Splicing mats a method for detecting differential alternative splicing between two rna seq samples 22. Alternative splicing as events are currently divided into five main types. Under the default setting mats tests the hypothesis that the difference in the exon inclusion levels of a given exon between sample 1 and 2 is above a user defined cutoff. Originally each mate length was 76 but after trimming it can be of any length.
We developed rmats a new statistical method for robust and flexible. To compare alternative splicing patterns between two samples for each exon we define and as its exon inclusion levels in sample 1 and 2.