Maternal Floor Infarction Treatment
Histological definitions association with intrauterine fetal growth restriction and risk or recurrence.
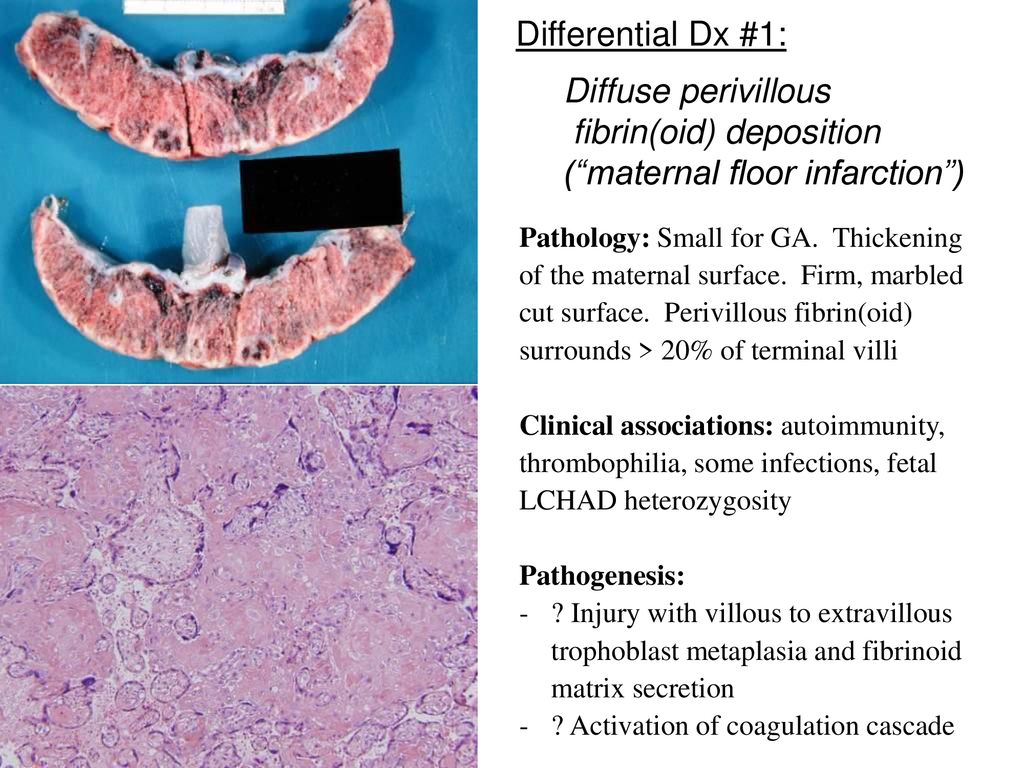
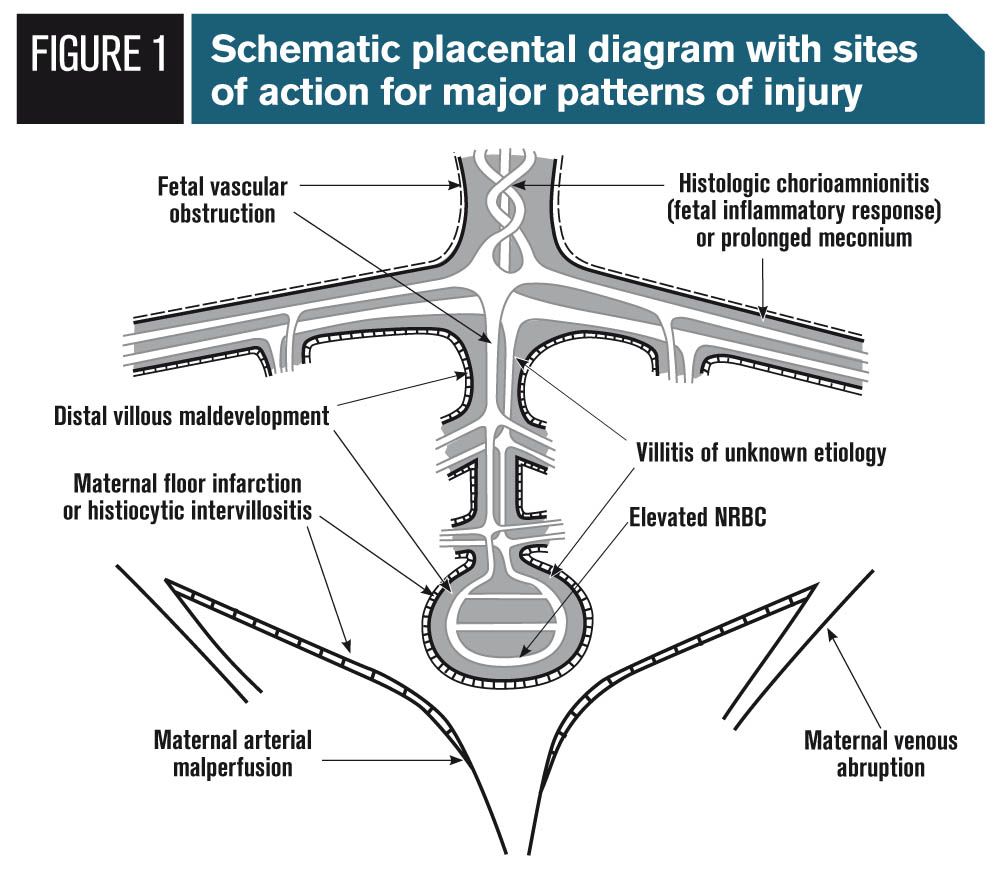
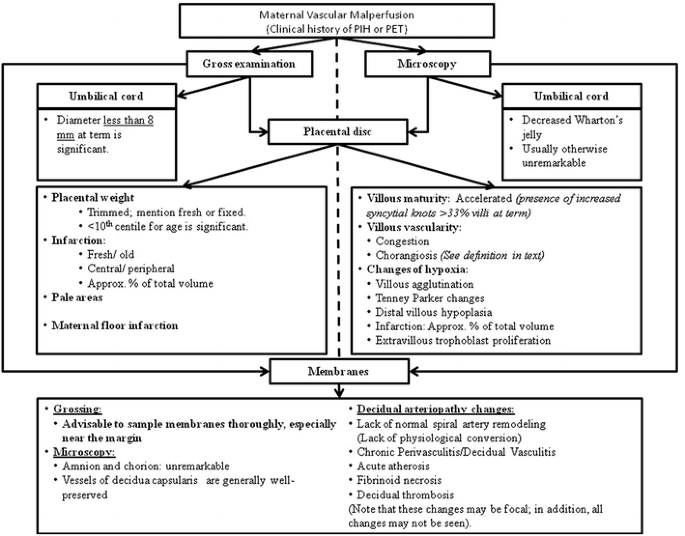
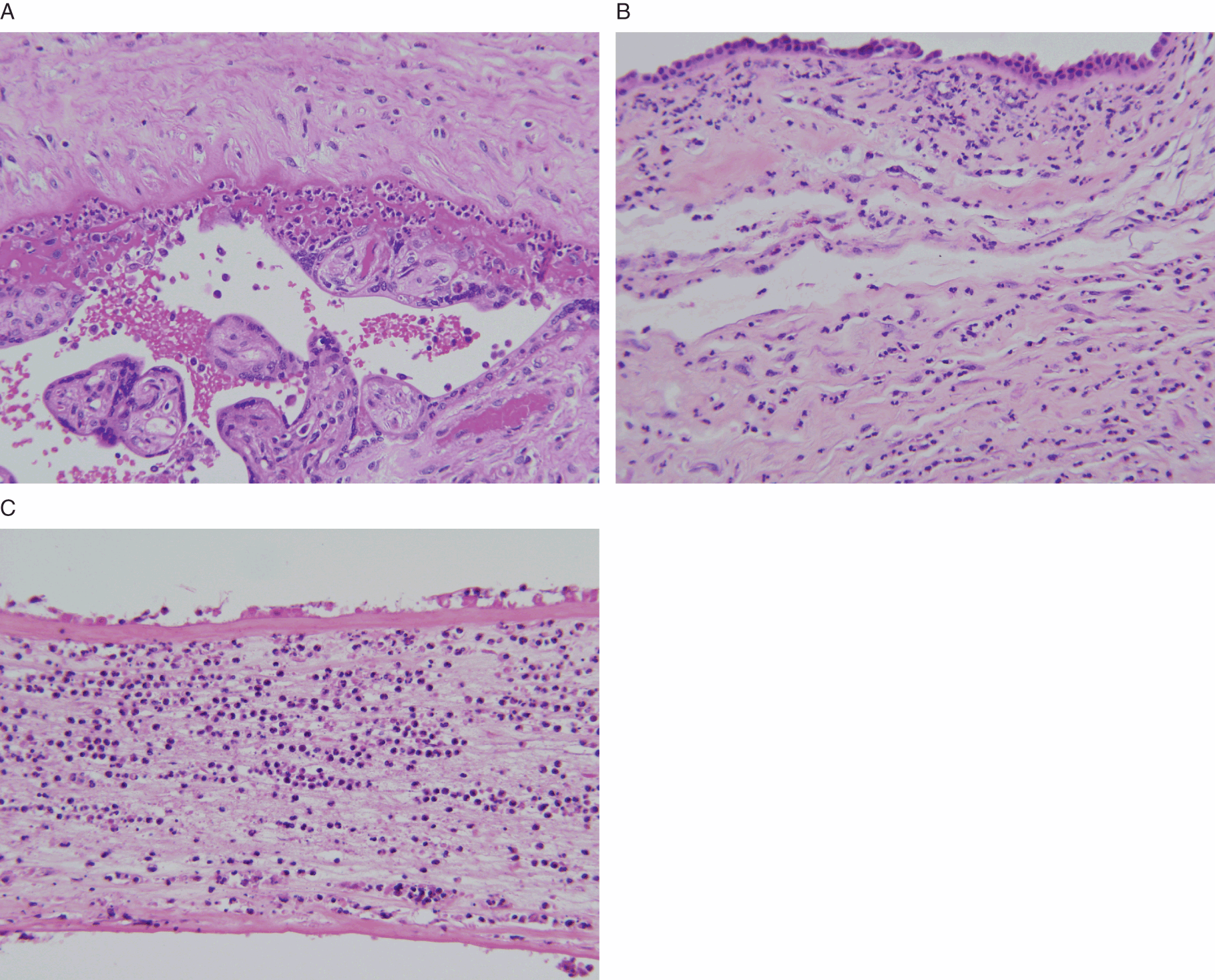
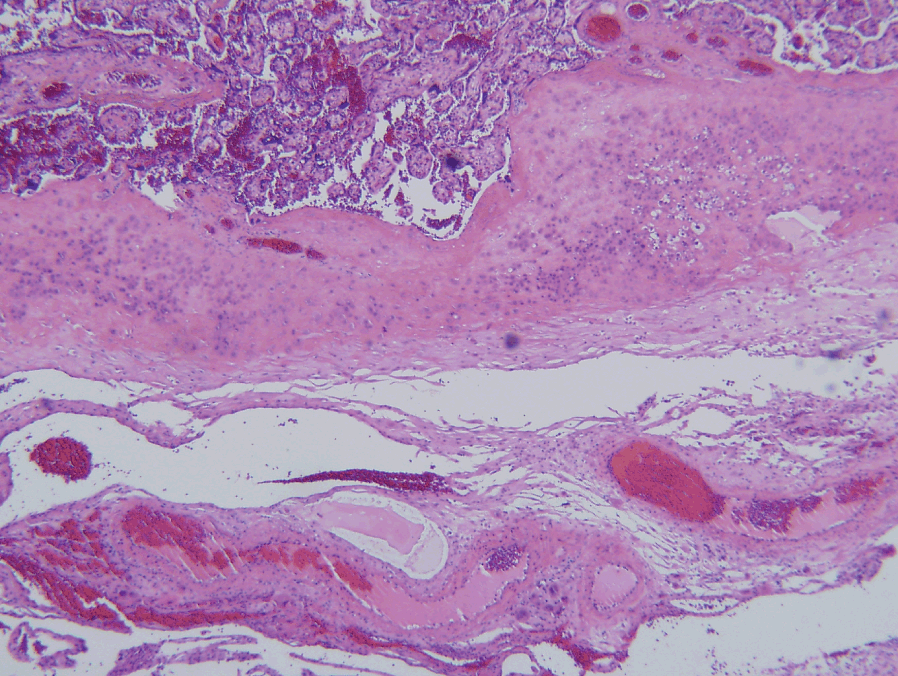
Maternal floor infarction treatment. Maternal floor infarction causes iugr and intrauterine fetal death with a reported risk of 69 and 40 respectively. The enveloped villi become atrophic and avascular. Maternal floor infarction also known as massive diffuse perivillous fibrin deposition is an uncommon idiopathic placental disorder with characteristic macroscopic and histologic findings. Maternal floor infarction abbreviated mfi is a pathology of the placenta.
The recurrence rate varies from 14 to 39. Tsang et al intravenous immunoglobulin in antiphospholipid syndrome and maternal floor infarction when standard treatment fails. Maternal floor infarction mfi is an uncommon placental disease associated with recurrent third trimester fetal loss and intrauterine growth retardation iugr usually severe. A maternal floor infarction then should show fibrin or matrix thickening of the maternal surface with otherwise typical changes of infarction in the villi.
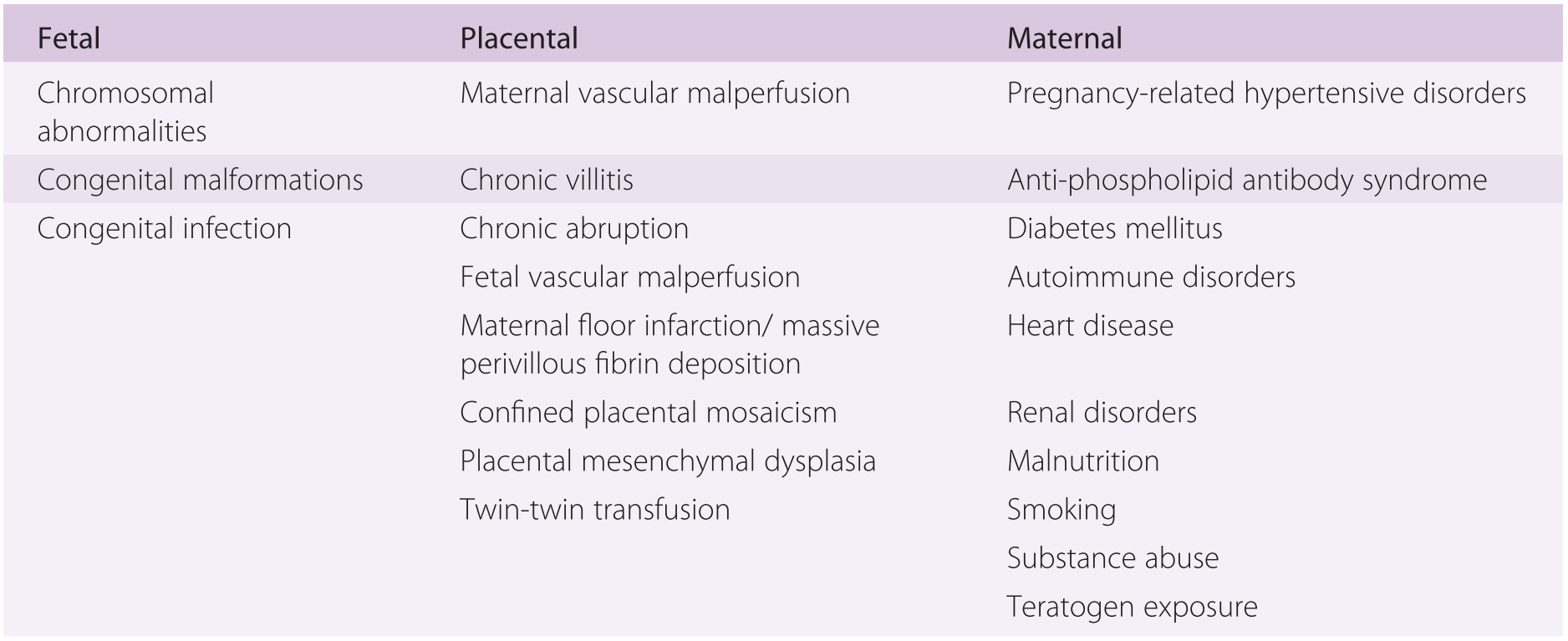
A case report am j perinatol 23 2006 pp. It is moot whether such a lesion which i will call true maternal floor infarction occurs but the term maternal floor infarction is not usually used in this sense. It is an important cause of adverse outcome in the fetus including intrauterine growth restriction premature delivery fetal death and neurologic injury. It is formally known as placental maternal floor infarction it is also known as massive perivillous fibrin deposition.
It has a very high recurrence rate and carries a significant risk or fetal demise. Maternal floor infarction and massive perivillous fibrin deposition. Placenta maternal floor infarction. The disease is characterized by extensive fibrin deposition in the intervillous spaces.
This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. Maternal floor infarction has important implications for the fetus that extend beyond the perinatal period.