Maternal Floor Infarction Cause

Vernof kk et al.
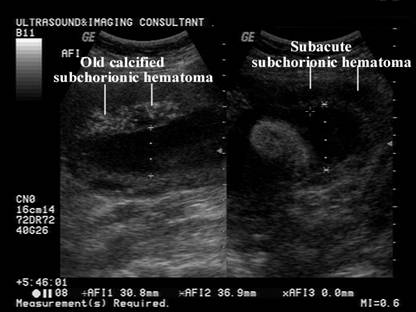
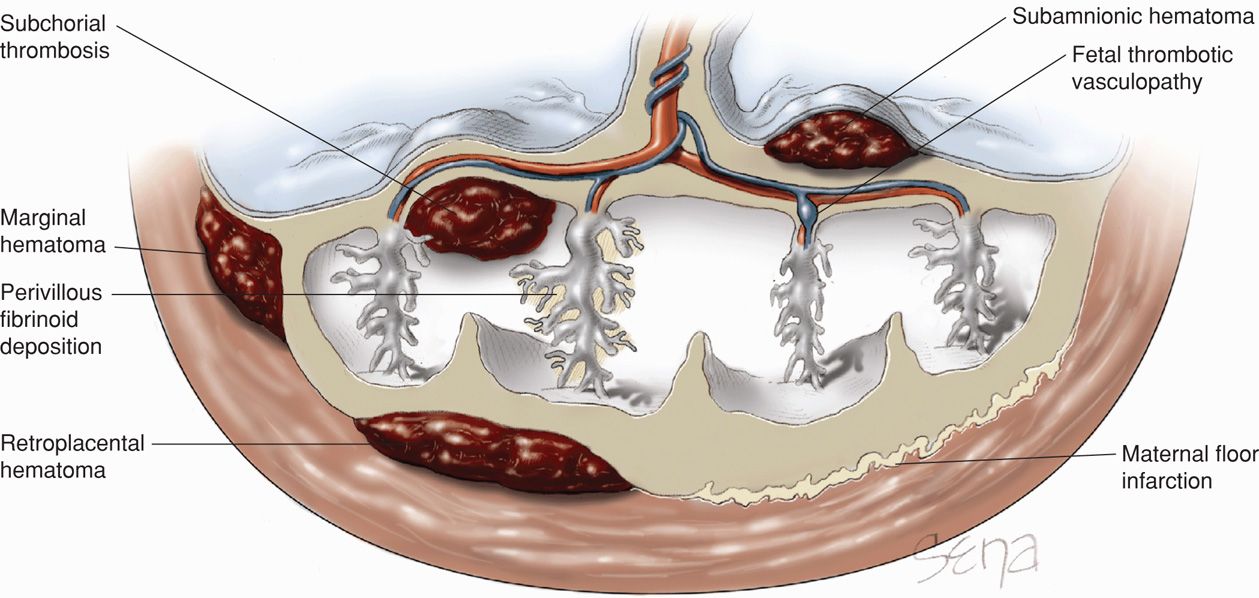
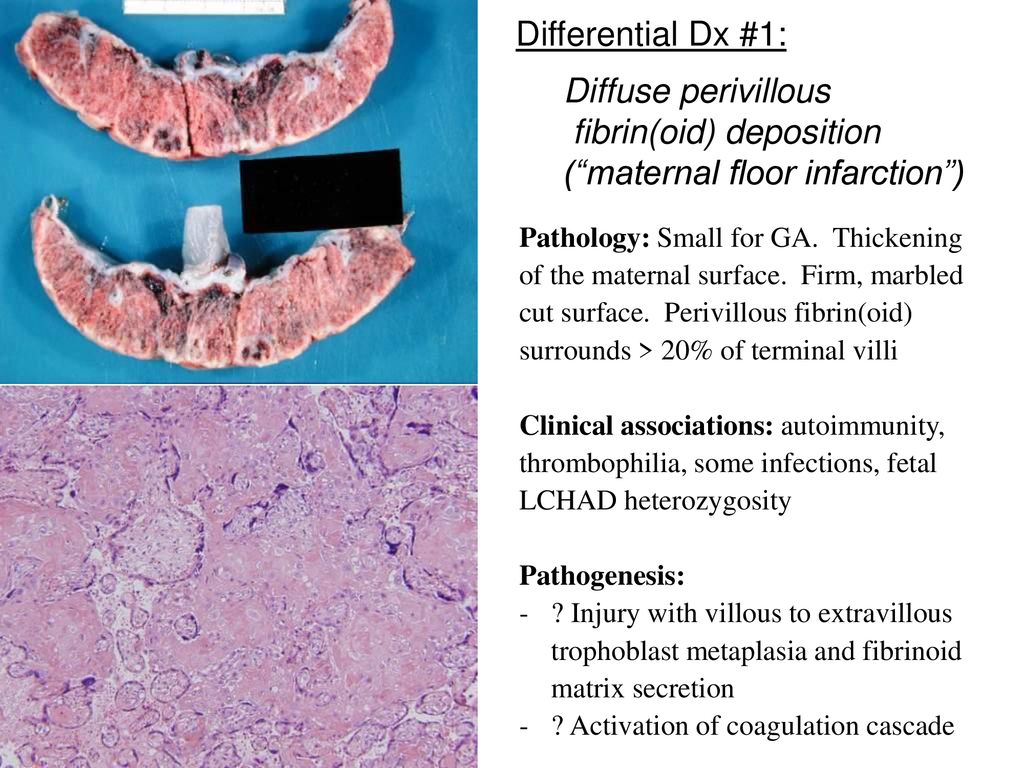
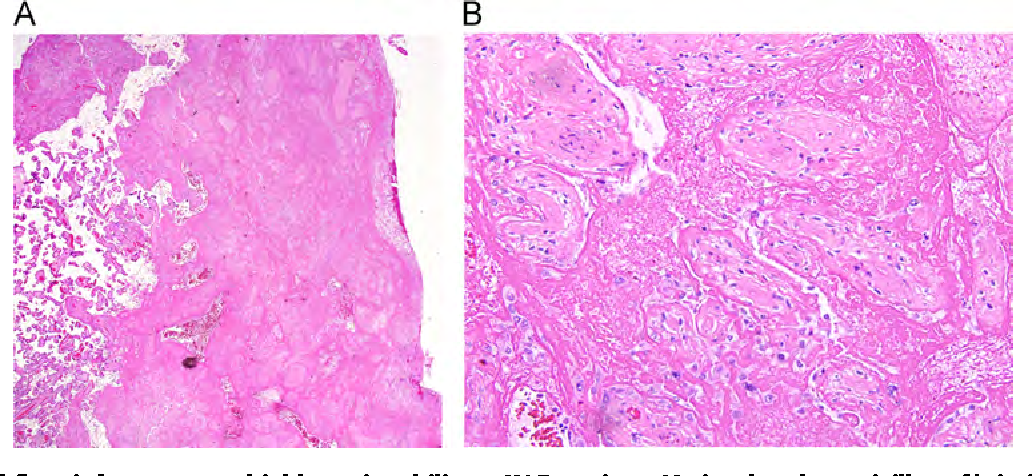
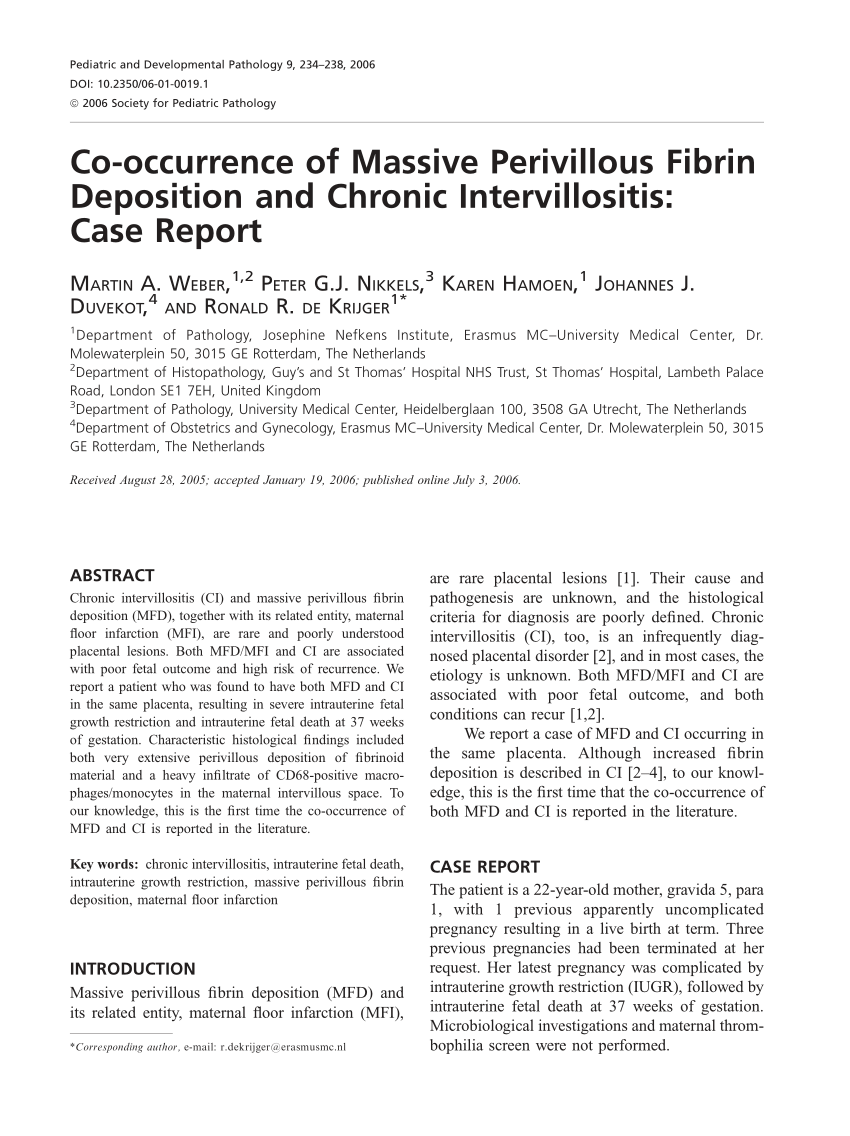
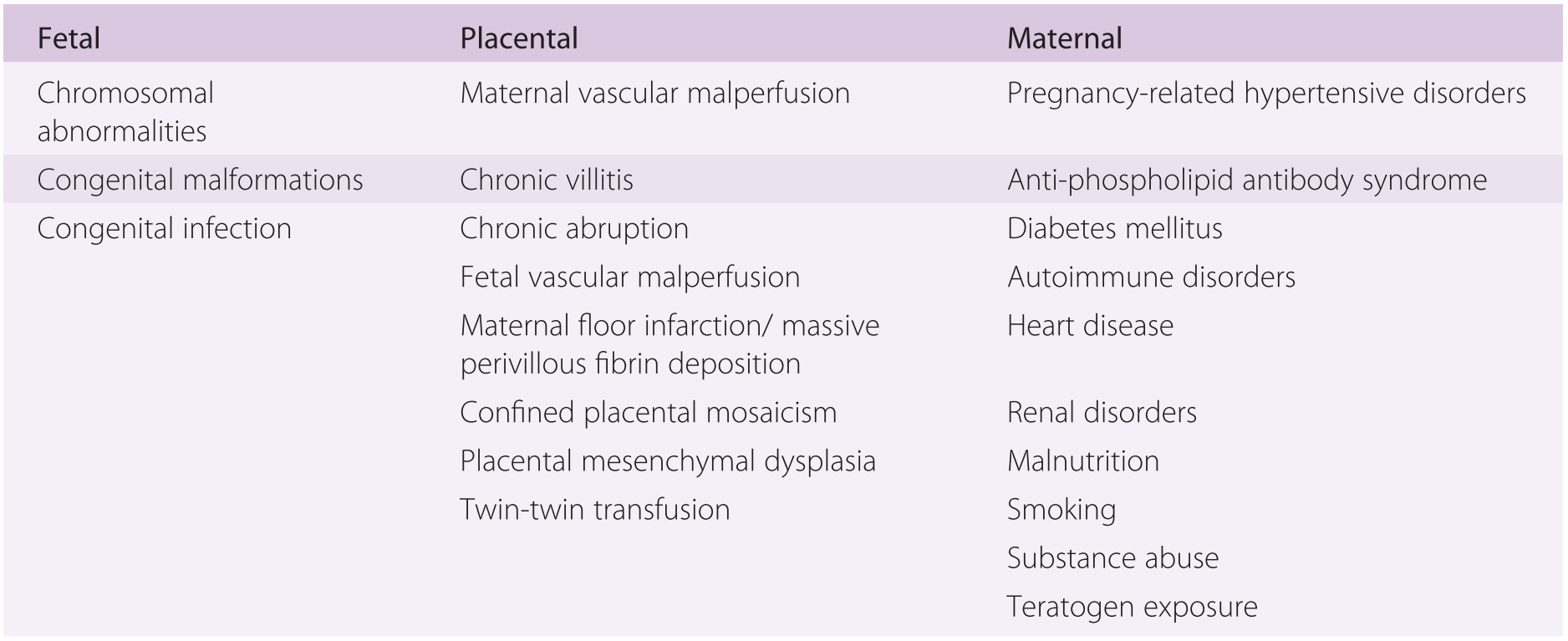
Maternal floor infarction cause. Maternal floor infarction abbreviated mfi is a pathology of the placenta. Manchesterrecurrent maternal floor infarction. Maternal floor infarction also known as massive diffuse perivillous fibrin deposition is an uncommon idiopathic placental disorder with characteristic macroscopic and histologic findings. Maternal floor infarction is a rare placental lesion of unknown etiology and is often associated with sudden intrauterine fetal demise and intrauterine growth restriction.
It is moot whether such a lesion which i will call true maternal floor infarction occurs but the term maternal floor infarction is not usually used in this sense. Relationship to x cells major basic protein and adverse perinatal outcome. Placenta maternal floor infarction. 1 3 the condition has been infrequently discussed in the obstetric or pathology literature and essentially no information is available in pediatric or genetic journals.
When volume of infarcts is over 50 of placental volume think of lupus anticoagulant. This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. An unusual cause of intrauterine growth retardation. And such are most often associated with pre eclampsia particularly the hellp syndrome variety hemolysis elevated lfts low platelets with rbc fragments.
A maternal floor infarction then should show fibrin or matrix thickening of the maternal surface with otherwise typical changes of infarction in the villi. Am j dis child. Placental dysfunction appears late in the process of the disease and the lesion develops rapidly within hours. It is formally known as placental maternal floor infarction it is also known as massive perivillous fibrin deposition.
Maternal floor infarction posted on october 26 2015 by luke s mom on thursday oct. 15 my doctor called with the results of my clotting disorder tests and luke s autopsy clotting disorders such as a factor v or factor ii mutation are one cause of stillbirths. A preventable cause of fetal death am j obstet gynecol 147 1983 pp.