Mat Calculation Under Ind As

Mat a brief introduction.
Mat calculation under ind as. Book profit of the company is rs. Any agreement under sub section 1 of section 90a and. The tax liability of a company will be higher of. Book profit of the financial year in which the asset is retired disposed realised or otherwise.
In many cases there have been significant regulatory challenges such as power and infrastructure companies potentially meeting the criteria for nbfcs. 28 40 000 will amount to rs. Items under heading items that will be reclassified to profit or loss will automatically be included for mat calculation as and when they are reclassified as profit loss in accordance with relevant ind as since they will not meet the condition of clause i of explanation 1 of 115jb 2. Abhishek gautam under secretary to the government of india.
For example a company following december ending will be required to prepare accounts for mat purposes under indian gaap for 9 months upto december 2016 and under ind as for 3 months thereafter. The transition amount will be calculated with reference to 1st january 2017. Hence the transition amount will be adjusted 1 5 th each year in 2017 18 to 2021 22. Minimum alternative tax is payable under the income tax act.
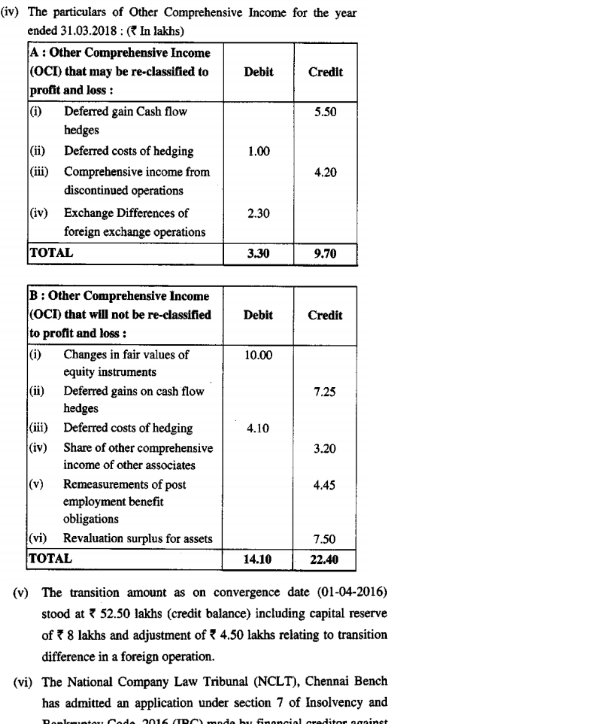
Being taxed under mat provisions. Under ind as total comprehensive income has two components profit or loss and oci all notional unrealised gains included in oci are required to be excluded for the purposes of arriving at free reserves section 2 43 distributable profits for payment of dividend section 123 and calculation. The transition amount will be calculated with reference to 1st january 2017. As the book profit based on ind as compliant financial statement is likely to be different from the book profit based on existing indian gaap the cbdt constituted a committee in june 2015 for suggesting the framework for computation of mat liability under section 115jb for ind as compliant companies in the year of adoption and thereafter.
Then the transition amount will be adjusted under mat equally in five consecutive years starting from 2017 18. The concept of mat was introduced to target those companies that make huge profits and pay the dividend to their shareholders but pay no minimal tax under the normal provisions of the income tax act by taking advantage of the various deductions and exemptions allowed under the act. I normal tax liability or ii mat. Dividend on preference shares whether classified as interest costs or dividend under ind as would be considered as dividend for the purpose of mat computation and needs to be added back to book profit for the purpose of mat computation.
Normal tax rate applicable to an indian company is 30 plus cess and surcharge as applicable. Tax 30 on rs.