Mat Alpha Yeast

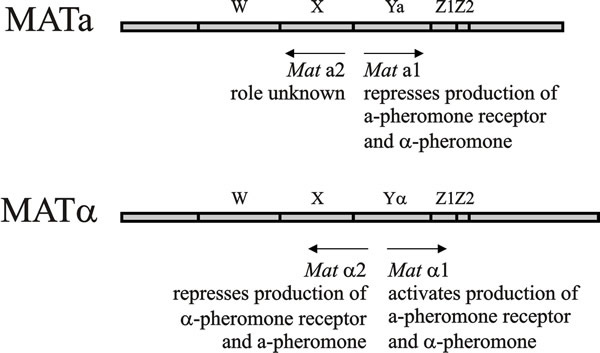
Mat alpha encodes two transcription factors alpha 1 and alpha 2.
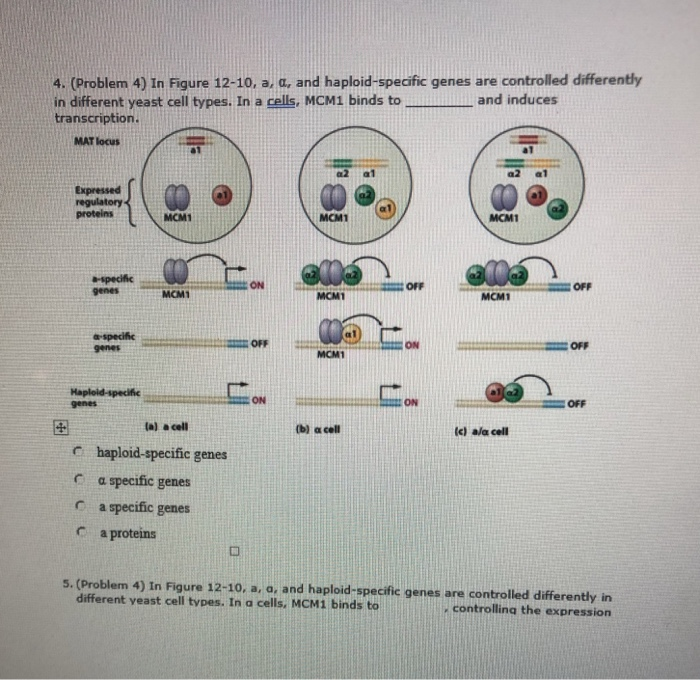
Mat alpha yeast. Europe pmc free article google scholar baker re gabrielsen o hall bd. Transcription factor mcm1 binds with alpha 1 to promoters of alpha specific genes and activates their transcription. 2 and corresponding receptors specific for each pheromone. Simplified chemical structures of yeast pheromones.
Evidence for two blocks to expression in mata mat alpha diploids. Mating type factors of yeast specify peptide hormones. Haploid yeast can fuse to form a diploid when cells of opposite mating type termed a and alpha are mixed. The mating of yeast only occurs between haploids which can be either the a or α alpha mating type and thus display simple sexual differentiation.
Ammerer g sprague gf jr bender a. Proc natl acad sci u s a. Homozygous diploid collection yeast heterozygous diploid collection yeast mat a or mat alpha haploid collections yeast essential collection. Definitionandmutantphenotype saccharomycescerevisiae baker syeast canexistineither ahaploid 1n oradiploid 2n state haploidsexpressone of two mating types a or a alpha.
Diploid cells are normally heterozygous a alpha at the mat locus 4 2 5. Control of yeast alpha specific genes. Transcriptional coactivator that in alpha cells binds cooperatively with mcm1 and ste12 to a dna sequence termed the qp element to activate the transcription of alpha specific genes. Mcm1 and alpha 2 bind to promoters of a specific genes and represses their transcription.
Mating type is determined by a single locus mat which in turn governs the sexual behaviour of both haploid and diploid cells. Mating type proteins are sequence specific dna binding proteins that act as master switches in yeast differentiation by controlling gene expression in a cell type specific fashion. The library consists of 4 828 mat alpha haploid clones 4 848 mat a haploid clones 5 996 heterozygous diploid clones and 4 741 homozygous diploid clones. The intent of this consortium was to produce a deletion clone for each gene in the yeast genome.
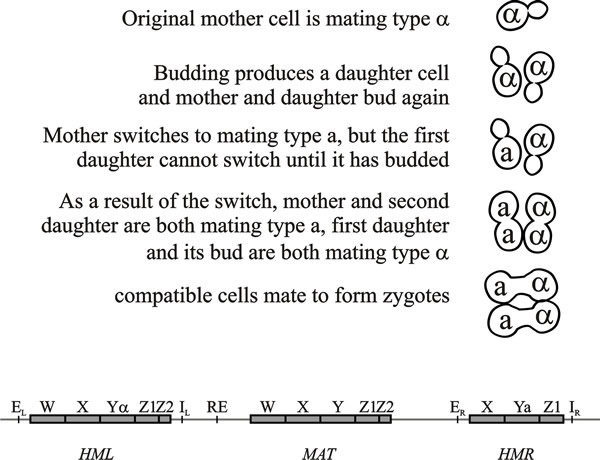
Some yeast are capable of switching mating type a process involving gene replacement by information from silenced copies of the mating type locus found elsewhere in the genome.